Diamonds

Note the colours, the diamond is like a prism (the effect is called fire). Look for flaws mostly in the top left. One is clearly visible near the centre Click here for larger image, opens in a new tab.

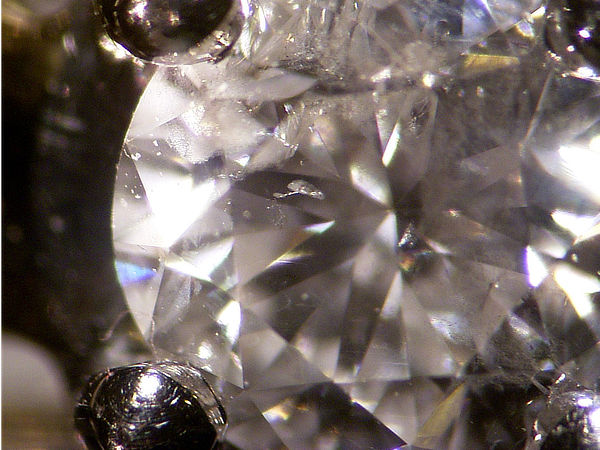
A diamond fresh from the ground. The small triangles are the crystal facets. This diamond won't be cut for jewellery, it has too many flaws and inclusions. Click here for larger image.
And click here for the same stone from a different angle. Pictures open in a new tab.
In brief
Diamonds are crystalised carbon.
Graphite (the lead in pencils) is also crystalised carbon, but a different crystal form.
Diamonds will burn (please don't try this at home!)
A diamond was believed to protect the wearer from the Devil, as well as the Plague.
Index
Cutting diamonds to make them look good
Artificial treatments to improve the way a diamond looks
Introduction
Diamonds are very hard, but like many other gemstones they are somewhat brittle, so a violent blow can crack or chip the stone. We see many old rings, and often the diamonds are damaged.
Over 120 miles (200km) below the earth's surface and upto 3
billion years ago, temperatures of 1100C and the incredible
pressure of 65,000 atmospheres allowed diamonds to form.
Aeons later, rocks like Kimberlite transported these precious
stones towards the surface.
Diamonds are (as we all know) the
hardest natural substance, so can be used for cutting any material; they
were used to cut the intricate marble designs on the Taj Mahal.
When I
first became interested in jewellery, I did not appreciate diamonds.
However admiring their beauty under the microscope, and seeing these various
inclusions and the beauty of their crystal structure has resulted in my coming
to regard them among the very best of gems.
Lab grown diamonds
 With a special lighbox and an app on a phone with a good camera, we can identify lab-grown diamonds
With a special lighbox and an app on a phone with a good camera, we can identify lab-grown diamonds
Top A natural diamond looks blue.
Centre A lab grown cvd diamond is green
Bottom A labgrown hpht diamond is red, this is the earlier type of synthetic diamond
They are a lot cheaper than natural diamonds.
The high price of natural stones shows that most customers prefer them.
If you're buying second hand, watch out. We've been approached several times by owners wanting to sell rings
with lab grown diamonds. The owners did not disclose the stones weren't natural.
They really are a risk if you're buying.
Some sellers do not state the diamonds are natural,
perhaps they don't test the stones. We test most diamonds, and include a message on our online shop
that the stones are natural (or lab grown if that's the case). If you're in our shop, ask and we can check for you.
Normally lab grown diamonds are clearly labelled.
Cutting and Shaping Diamonds
Their hardness makes cutting the facets, which cause the sparkle and fire,
very difficult. Faceted stones have only been around a few
hundred years. Finally in 1919 scientists worked
out how to maximise the sparkle and fire by cutting the facets at the perfect antle.
Diamonds can only be cut or polished by another diamond. This
works because diamonds are harder at some angles than others - a
result of the crystal structure. Before cutting, the craftsman
will ensure that no facets lie along this line of maximum
hardness - because these would be impossible to cut or polish.
Provided that particular angle is avoided some of the diamond
dust used for cutting and polishing will be harder than the
diamond which is being worked on.
Diamonds may look clear but actually they have varying tints from
blue white towards brown. Blue white commands the highest price.
Coloured stones do occur, and if attractive are very
valuable. Most diamonds are too flawed to be worn as
jewellery and are used in industry for cutting and grinding.